How to Install Wazuh Manager
Introduction
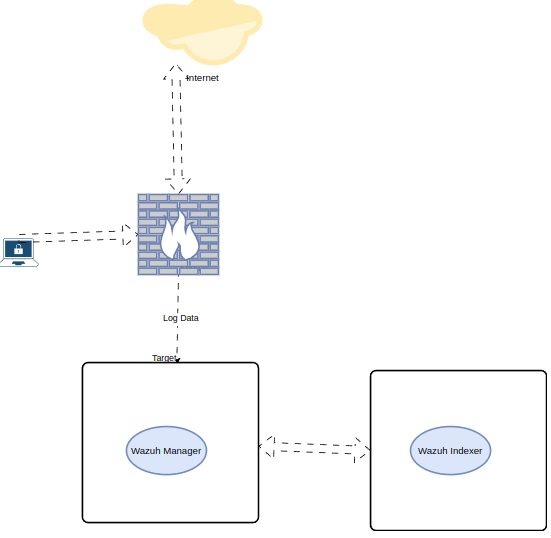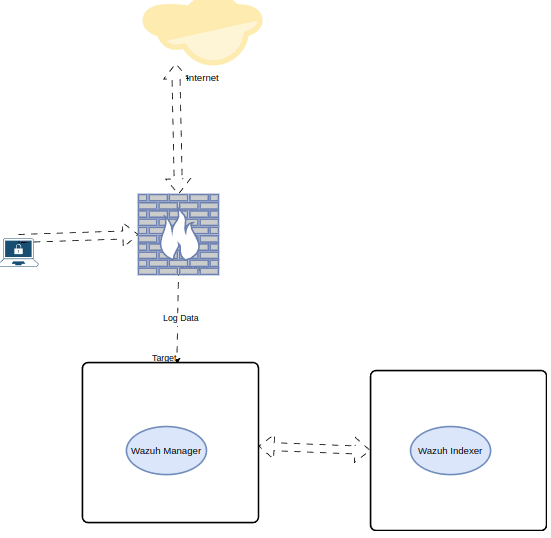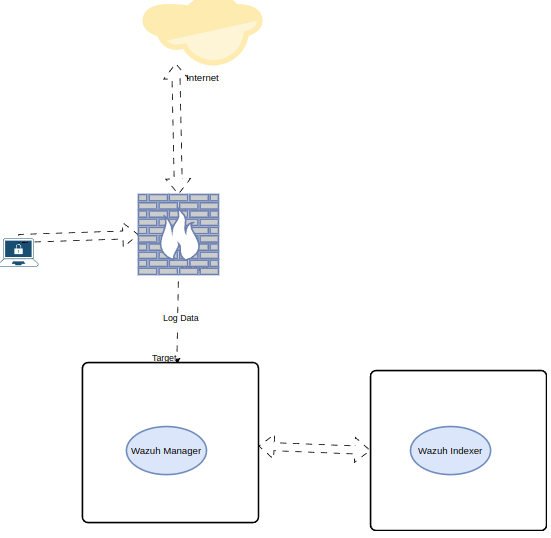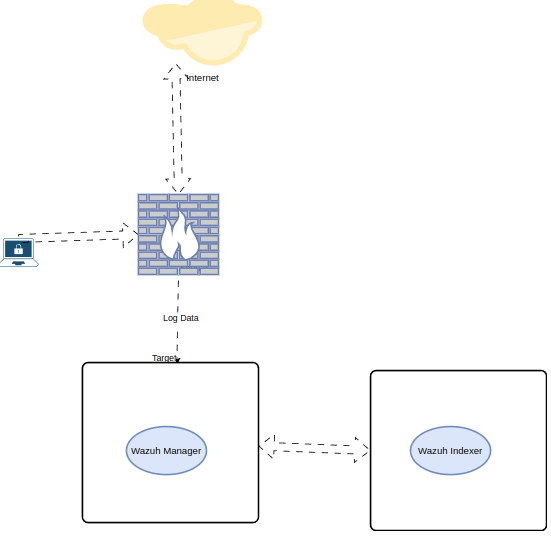 Installation
Let’s now install our wazuh-indexer . This is the component that will be responsible for storing all of our security events and logs. It is a fork of the ELK stack and is built on top of the OpenSearch project.
Installation
Let’s now install our wazuh-indexer . This is the component that will be responsible for storing all of our security events and logs. It is a fork of the ELK stack and is built on top of the OpenSearch project.
Certificates Creation Download the wazuh-certs-tool.sh script and the config.yml configuration file. This creates the certificates that encrypt communications between the Wazuh central components.
You can also use your own internal PKI if desired. Wazuh provides an easy to use bash script that we will use to generate our own internal certs to encrypt logs being sent to the wazuh-indexer .
curl -sO https://packages.wazuh.com/4.3/wazuh-certs-tool.sh curl -sO https://packages.wazuh.com/4.3/config.yml Edit ./config.yml and replace the node names and IP values with the corresponding names and IP addresses. You need to do this for the Wazuh indexer, the Wazuh dashboard nodes, and any servers that will be sending logs to the wazuh-indexer such as Graylog (if you are following our World’s Best Open Source SOC series).
nodes:
# Wazuh indexer nodes
indexer:
- name: node-1
ip: <indexer-node-ip>
# - name: node-2
# ip: <indexer-node-ip>
# - name: node-3
# ip: <indexer-node-ip>
# Wazuh server nodes
# Use node_type only with more than one Wazuh manager
server:
- name: wazuh-1
ip: <wazuh-manager-ip>
# node_type: master
# - name: wazuh-2
# ip: <wazuh-manager-ip>
# node_type: worker
# Wazuh dashboard node
dashboard:
- name: dashboard
ip: <dashboard-node-ip>
Run the ./wazuh-certs-tool.sh to create the certificates. For a multi-node cluster, these certificates need to be later deployed to all Wazuh instances in your cluster.
bash ./wazuh-certs-tool.sh -A
tar -cvf ./wazuh-certificates.tar -C ./wazuh-certificates/ .
Install
apt-get install debconf adduser procps
Install the following packages if missing.
apt-get install gnupg apt-transport-https
Install the GPG key.
curl -s https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH | gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg --import && chmod 644 /usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg
Add the repository.
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg] https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/apt/ stable main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wazuh.list
Update the packages information.
apt-get -y install wazuh-indexer
Edit /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml and replace the following values:
network.host: Sets the address of this node for both HTTP and transport traffic. The node will bind to this address and will also use it as its publish address. Accepts an IP address or a hostname. Use the same node address set in config.yml to create the SSL certificates. node.name: Name of the Wazuh indexer node as defined in the config.yml file. For example, node-1. cluster.initial_master_nodes: List of the names of the master-eligible nodes. These names are defined in the config.yml file. Uncomment the node-2 and node-3 lines, change the names, or add more lines, according to your config.yml definitions. cluster.initial_master_nodes:
- "node-1"
- "node-2"
- "node-3"
- discovery.seed_hosts: List of the addresses of the master-eligible nodes. Each element can be either an IP address or a hostname. You may leave this setting commented if you are configuring the Wazuh indexer as a single-node. For multi-node configurations, uncomment this setting and set your master-eligible nodes addresses.
discovery.seed_hosts:
- "10.0.0.1"
- "10.0.0.2"
- "10.0.0.3"
- plugins.security.nodes_dn: List of the Distinguished Names of the certificates of all the Wazuh indexer cluster nodes. Uncomment the lines for node-2 and node-3 and change the common names (CN) and values according to your settings and your config.yml definitions.
plugins.security.nodes_dn:
- "CN=node-1,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US"
- "CN=node-2,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US"
- "CN=node-3,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US" Run the below command to view your certs CN
openssl x509 -subject -nameopt RFC2253 -noout -in hostname.pem
Run the following commands replacing <indexer-node-name> with the name of the Wazuh indexer node you are configuring as defined in config.yml. For example node-1. This deploys the SSL certificates to encrypt communications between the Wazuh central components.
NODE_NAME=<indexer-node-name>
Recommended action — If no other Wazuh components are going to be installed on this node, remove wazuh-certificates.tar running rm -f ./wazuh-certificates.tar to increase security.
Memory Locking Wazuh-indexermalfunctions when the system is swapping memory. It is crucial for the health of the node that none of the JVM is ever swapped out to disk. The following steps show how to set the bootstrap.memory_lock setting to true so wazuh-indexerwill lock the process address space into RAM. This prevents any wazuh-indexermemory from being swapped out.
Set bootstrap.memory_lock: Uncomment or add this line to the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml file:
bootstrap.memory_lock: true 2. Edit the limit of system resources:
nano /usr/lib/systemd/system/wazuh-indexer.service
Add the following lines to the file: [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity
- Limit memory
The previous configuration might cause node instability or even node death with an OutOfMemory exception if wazuh-indexer tries to allocate more memory than is available. JVM heap limits will help limit memory usage and prevent this situation. Two rules must be applied when setting wazuh-indexer's heap size:
- Use no more than 50% of available RAM.
- Use no more than 32 GB.
It is also important to consider the memory usage of the operating system, services and software running on the host. By default, wazuh-indexer is configured with a heap of 1 GB. It can be changed via JVM flags using the /etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options file: Xms represents the initial size of total heap space Xmx represents the maximum size of total heap space -Xms4g -Xmx4g Warning: The values min (Xms) and max (Xmx) sizes must be the same to prevent JVM heap resizing at runtime as this is a very costly process.
Let’s now start the service:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable wazuh-indexer
systemctl start wazuh-indexer
Cluster Initialization Run the Wazuh indexer indexer-security-init.sh script on any Wazuh indexer node to load the new certificates information and start the single-node or multi-node cluster. /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/indexer-security-init.sh
NOTE: You only have to initialize the cluster once, there is no need to run this command on every node.
Replace <WAZUH_INDEXER_IP> and run the following command to check if the single-node or multi-node cluster is working correctly.
curl -k -u admin:admin https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP>:9200/_cat/nodes?v
Now lets install the Wazuh-Dashboards that provides us a WebUI to interact with our Wazuh-Indexer cluster.
How to Install Wazuh-Dashboard
The Wazuh dashboard is a flexible and intuitive web user interface for mining, analyzing, and visualizing security events and alerts data. It is also used for the management and monitoring of the Wazuh platform. Additionally, it provides features for role-based access control (RBAC) and single sign on (SSO).
Documentation: https://documentation.wazuh.com/current/getting-started/components/wazuh-dashboard.html
This also provides a WebUI that allows us to interact with the wazuh-indexer nodes in an easier way.
https://documentation.wazuh.com/current/getting-started/components/wazuh-dashboard.html Architecture The wazuh-dashboards service will need to communicate with our previously deployed wazuh-indexer cluster. This can either be installed onto a node already running the wazuh-indexer , or deployed onto a dedicated server.
Installation Install the following packages if missing. apt-get install debhelper tar curl libcap2-bin 2. Install the GPG key.
curl -s https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH | gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg --import && chmod 644 /usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg 3. Add the repository.
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg] https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/apt/ stable main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wazuh.list 4. Update the packages information.
apt-get update 5. Install the Wazuh dashboard package.
apt-get -y install wazuh-dashboard
Configuration
Edit the /etc/wazuh-dashboard/opensearch_dashboards.yml file and replace the following values:
server.host: This setting specifies the host of the back end server. To allow remote users to connect, set the value to the IP address or DNS name of the Wazuh dashboard server. The value 0.0.0.0 will accept all the available IP addresses of the host.
opensearch.hosts: The URLs of the Wazuh indexer instances to use for all your queries. Wazuh dashboard can be configured to connect to multiple Wazuh indexer nodes in the same cluster. The addresses of the nodes can be separated by commas. For example, ["https://10.0.0.2:9200","https://10.0.0.3:9200","https://10.0.0.4:9200"]
server.host: 0.0.0.0
server.port: 443
opensearch.hosts: https://localhost:9200
opensearch.ssl.verificationMode: certificate
Deploying Certificates
Replace <dashboard-node-name> with your Wazuh dashboard node name, the same used in config.yml to create the certificates, and move the certificates to their corresponding location.
NODE_NAME=<dashboard-node-name>
Start the service:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable wazuh-dashboard
systemctl start wazuh-dashboard
Edit the file /usr/share/wazuh-dashboard/data/wazuh/config/wazuh.yml and replace the url value with the IP address or hostname of the Wazuh server master node.
hosts:
- default:
url: https://localhost
port: 55000
username: wazuh-wui
password: wazuh-wui
run_as: false
Securing the Installation On any Wazuh indexer node, use the Wazuh passwords tool to change the passwords of the Wazuh indexer users.
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/plugins/opensearch-security/tools/wazuh-passwords-tool.sh --change-all
On your Wazuh dashboard node, run the following command to update the kibanaserver password in the Wazuh dashboard keystore. Replace <kibanaserver-password> with the random password generated in the first step.
echo <kibanaserver-password> | /usr/share/wazuh-dashboard/bin/opensearch-dashboards-keystore --allow-root add -f --stdin opensearch.password
Restart the wazuh-dashboard.
systemctl restart wazuh-dashboard
Conclusion Throughout this post we discussed the components of our backend storage, architecture design, and installation steps. Our backend storage is a crucial link in our SIEM stack (arguably the biggest) as it allows us to store and view all of our collected security events.
It is imperative that we ensure a highly available cluster and proper system resource monitoring (CPU, RAM, Disk) when deploying in a production environment.
